As the world grapples with plastic pollution and the urgent need for sustainable alternatives, bioplastics have emerged as a promising solution. Among them, hemp-based bioplastics offer a unique combination of biodegradability, strength, and low environmental footprint. This article explores the science behind hemp bioplastics, their advantages, current applications, and potential role in India’s sustainable development goals.
The global plastic crisis is no longer a distant threat; it is an immediate reality. Traditional plastics, derived from fossil fuels, take hundreds of years to decompose and contribute massively to environmental degradation. The search for sustainable and biodegradable alternatives has led to growing interest in hemp-based bioplastics, a solution rooted in nature and innovation.
Hemp bioplastics are plastics derived from the cellulose content of the hemp plant (Cannabis sativa). The stalks of hemp are rich in cellulose — up to 65-70%, compared to 40-50% in wood — making it one of the most efficient plant sources for bioplastic production.
The cellulose is extracted, processed, and polymerized into bioplastic forms such as:
• Composite Bioplastics (hemp fibers combined with other biopolymers or resins)
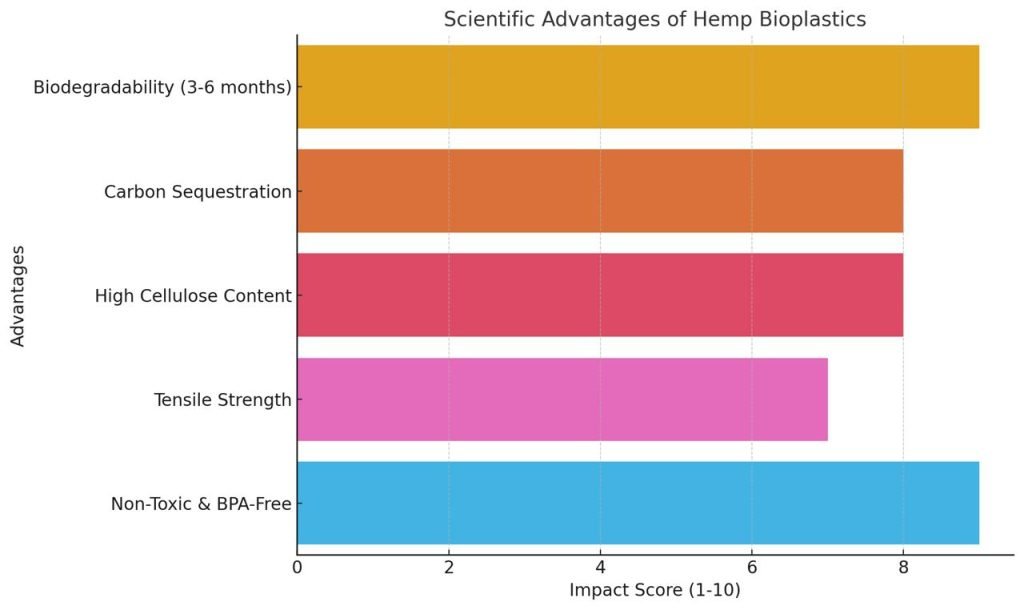
a) High Biodegradability
Hemp bioplastics can degrade within 3-6 months under industrial composting conditions, compared to petroleum-based plastics which can persist for 500+ years.
b) Reduced Carbon Footprint
Hemp sequesters more CO₂ per acre than most commercial crops. When used in bioplastics, this contributes to a net-negative carbon cycle.
c) Strong Mechanical Properties
When reinforced with hemp fibers, bioplastics show:
d) Non-Toxic & Renewable
Free of harmful additives like BPA and phthalates, hemp plastics are safe for both consumers and the environment.
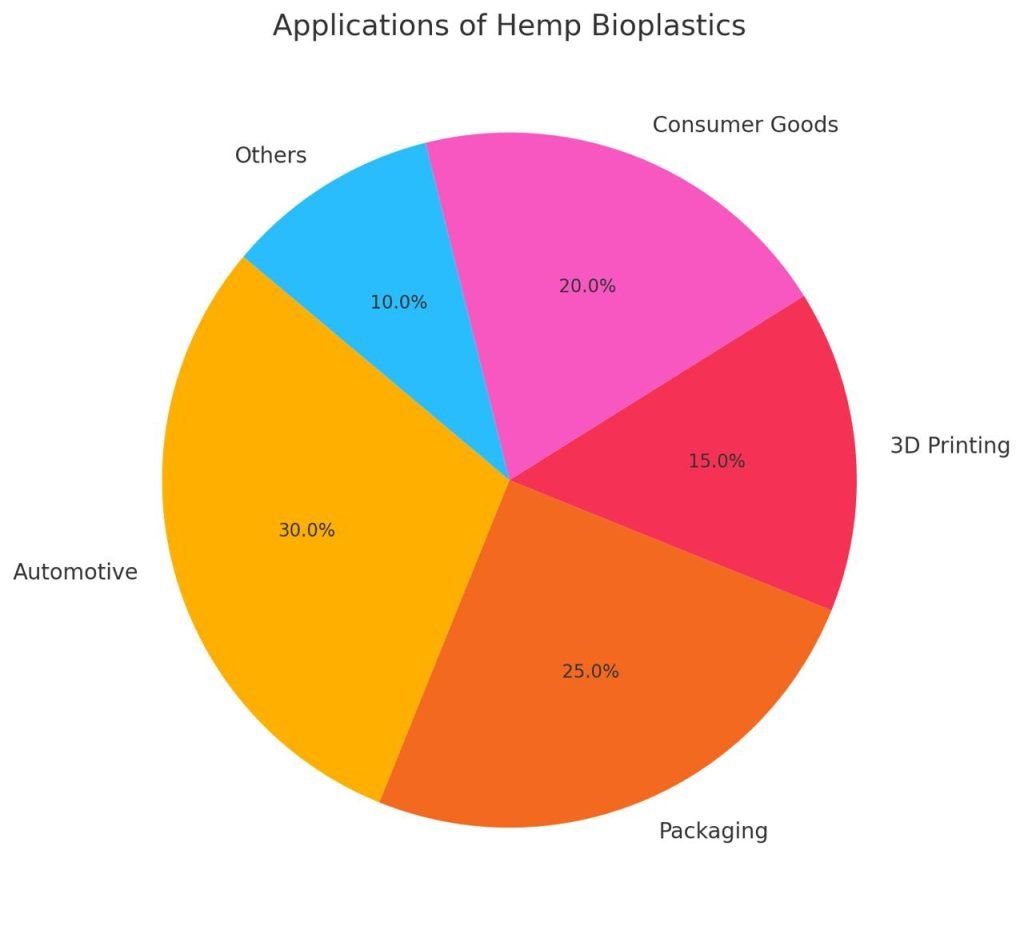
Automotive Industry
Companies like BMW and Mercedes-Benz are already using hemp fiber composites in dashboards and door panels.
Packaging
Hemp plastics offer a biodegradable alternative to single-use packaging — from bottles to containers and films.
3D Printing
Hemp PLA filaments are being used for eco-friendly prototyping in additive manufacturing.
Consumer Goods
Despite the promise, hemp bioplastics face certain limitations:
India, with its diverse agro-climatic zones, rising sustainability goals, and millions of small farmers, is uniquely positioned to become a global leader in hemp bioplastics. With government support for hemp research and industrialization, the nation can:
Innovations are underway to improve:
Collaborations between startups, researchers, and policymakers can accelerate the shift toward a hemp-based circular economy.
Hemp bioplastics represent a transformative intersection of science, sustainability, and economic potential. By investing in this green alternative today, we can move toward a future where plastic pollution is not just reduced — but reimagined.
(https://hempworks.in/blogs/from-the-journal/future-of-hemp-bioplastics-advantages-and-applications)


How we do it?
OUR VALUES
Why we do it?
OUR PROMISE
FAQ | LIBRARY | COURSES
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Refund and Returns Policy Shipping Policy